Canada’s Mortgage Renewal Crisis: What Happens When Rates Go Up?
For years, Canadians benefited from historically low mortgage rates. That financial comfort zone is ending. With rising interest rates driven by the Bank of Canada’s battle against inflation, a looming crisis is unfolding—the mortgage renewal crisis.
Millions of homeowners who secured low fixed rates during the pandemic are now approaching their renewal dates, only to find that their monthly payments could skyrocket. This article explores what happens when rates go up, how it impacts borrowers and the housing market, and what strategies can help navigate this financial storm.

What Is the Canada Mortgage Renewal Crisis?
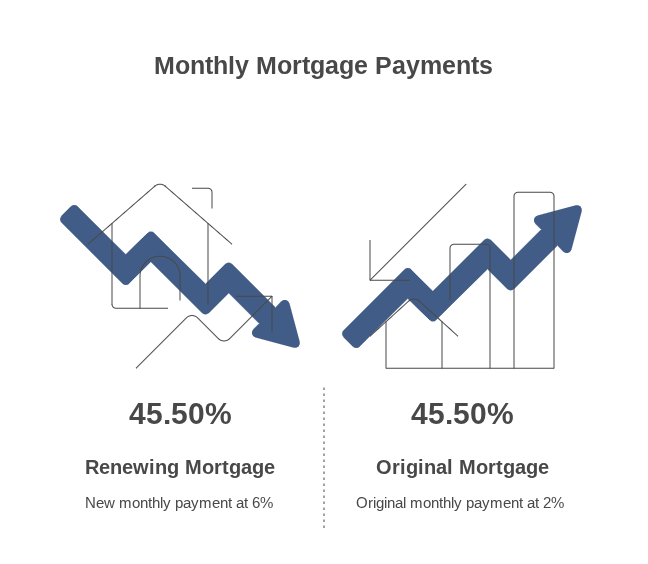
The mortgage renewal crisis refers to the financial distress faced by Canadians whose mortgage terms are ending just as interest rates have surged. Borrowers who once enjoyed rates as low as 1.5%–2.0% are now being offered renewal rates closer to 5.5%–6.5%.
According to the Bank of Canada, over $700 billion in mortgages are set to renew by the end of 2026. The majority of these are fixed-rate mortgages originated during the ultra-low-interest rate era of 2020–2021. These homeowners are now staring down the barrel of steep payment increases.
Why Are Interest Rates Rising in Canada?
Interest rates are rising as a tool to curb inflation. The Bank of Canada began raising its overnight lending rate aggressively from early 2022 onward to slow consumer spending and bring down inflation. While inflation has cooled slightly, interest rates remain high to maintain price stability.
This shift impacts variable and fixed mortgage rates alike, creating a tough renewal environment for borrowers who originally locked in during the low-rate cycle.
The Real Impact: How Rate Hikes Affect Homeowners
1. Increased Monthly Mortgage Payments
A homeowner with a $400,000 mortgage at 2% would pay about $1,690 monthly. Renewing at 6% increases that payment to approximately $2,560—a rise of over $870 per month.
This is not a hypothetical scenario. Across Canada, similar payment shocks are becoming the norm.
2. Budget Squeeze and Lifestyle Changes
Higher mortgage costs force families to cut discretionary spending, pause investments, or dip into emergency savings. Some may need to delay retirement contributions, cancel vacations, or reduce childcare expenses.
3. Increased Risk of Defaults
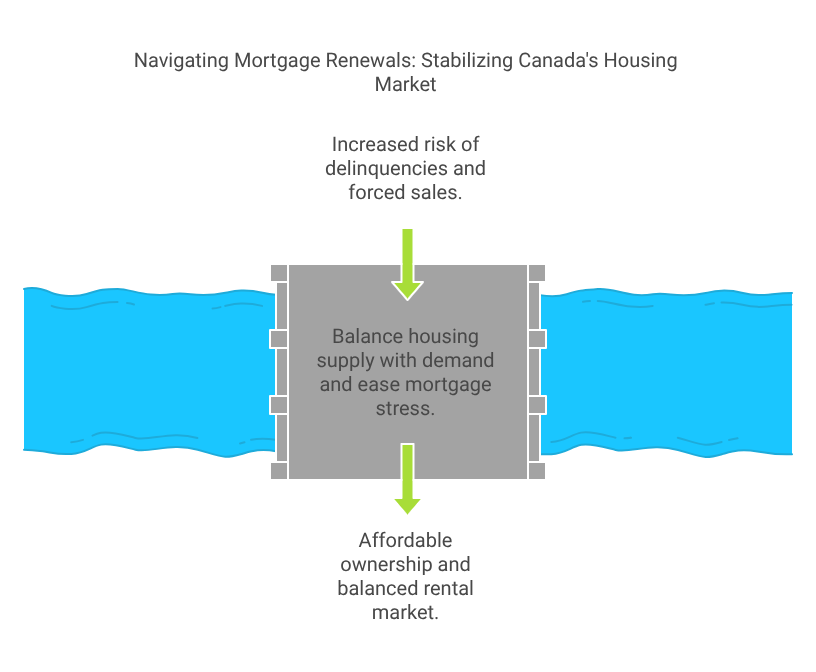
With more income going to housing, debt-to-income ratios are rising. Those already stretched thin could struggle to make payments, leading to higher risks of mortgage delinquency or forced property sales.
How the Mortgage Renewal Crisis Is Changing the Housing Market
Price Pressure and Reduced Demand
As more homeowners look to offload properties due to unaffordable renewals, housing supply increases. Meanwhile, demand weakens as buyers struggle to qualify under the mortgage stress test, now calculated with higher rates.
This imbalance is creating downward pressure on home prices, especially in high-debt cities like Toronto and Vancouver.
A Shift from Ownership to Renting
With fewer Canadians able to afford ownership, demand for rentals is surging. This puts pressure on the rental market, driving up rents and making affordability worse across the board.
Slower Sales and Construction
Real estate sales have slowed in many regions, and new home construction is also cooling as developers hesitate to build in an uncertain market. This could result in longer-term housing supply issues if not addressed.
Who’s Most Affected by Mortgage Renewals?
Fixed-Rate Mortgage Holders (2020–2021)
These borrowers secured low rates during the pandemic. Now, they face the steepest increases in monthly payments as their terms expire.
Variable-Rate Mortgage Holders
While some have already seen payments rise with the prime rate, others may hit their trigger rate, where payments no longer cover interest, resulting in increased debt or forced payment hikes.
Highly Indebted Borrowers
Homeowners with large mortgage balances relative to income are at greater risk of financial strain, especially in high-cost cities. Renewal could push their finances past the tipping point.

The Bank of Canada’s Position
Despite pressure, the Bank of Canada is holding firm in its tight monetary policy, indicating that interest rates will likely remain high through 2025. The central bank’s priority remains keeping inflation within its 2% target band.
While this strategy may stabilize prices over time, it comes at the cost of increased household financial stress.
Government and Financial Sector Responses
Limited Federal Intervention
While programs exist for first-time buyers and debt relief, there are no broad measures addressing mortgage renewal hardship. Critics argue that more targeted intervention is needed for those facing payment shocks.
Lender Flexibility
Some banks and credit unions are offering temporary relief options, such as:
- Extending amortization periods
- Interest-only payment options
- Payment deferrals
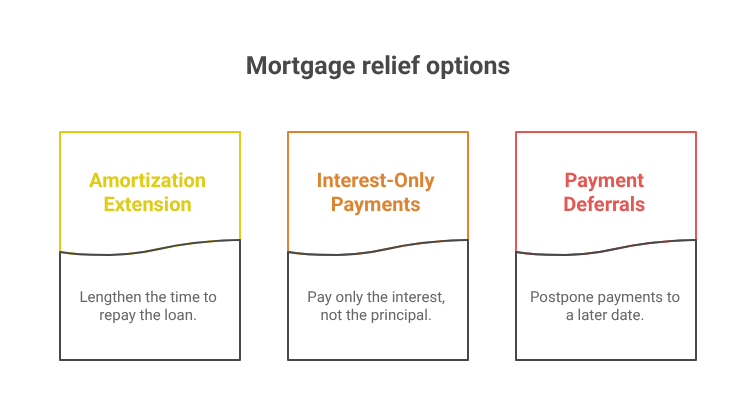
While helpful in the short term, these solutions often result in higher interest costs over time.
What Homeowners Can Do Right Now
1. Start Early
Don’t wait until your mortgage term expires. Most lenders allow renewals up to 120–180 days in advance. Locking in early could protect you from additional rate increases.
2. Shop Around
Don’t settle for the first offer. Use mortgage brokers or online comparison tools to find the most competitive rates and terms that suit your financial situation.
3. Consider a Longer Amortization
Increasing your amortization period (e.g., from 25 to 30 years) reduces monthly payments, even if total interest increases over time. It can be a useful tool for budget management.
4. Refinance Strategically
If you have home equity, refinancing can consolidate higher-interest debt or create room for financial flexibility. Just ensure you understand the costs and risks involved.
5. Improve Your Credit Profile
A better credit score can help you secure lower rates. Pay bills on time, reduce credit card balances, and avoid opening new credit lines before renewal.
What Happens If You Can’t Afford Your Renewal?
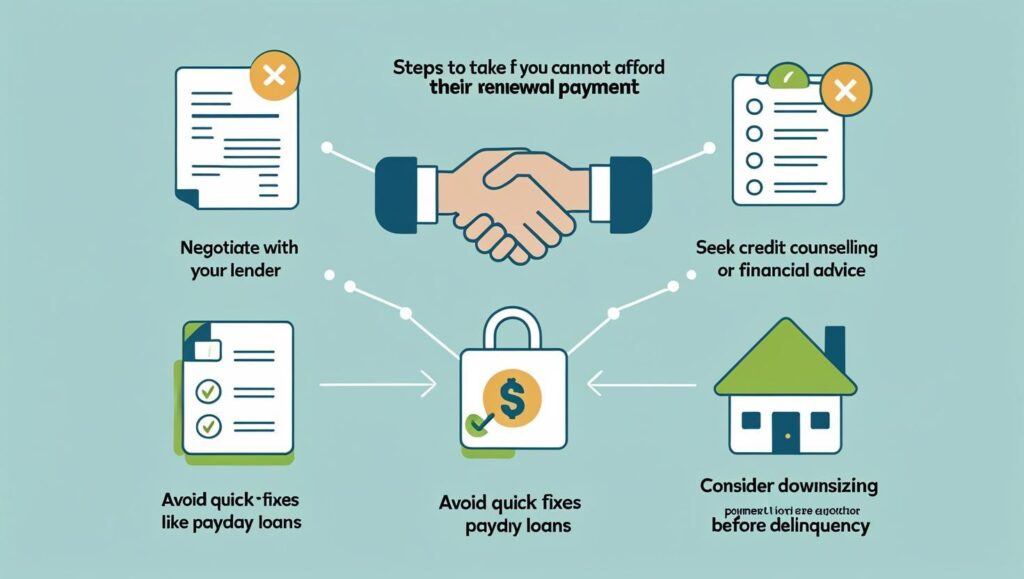
If your renewal quote is beyond your means:
- Negotiate with your lender. Many institutions will try to work out a payment plan rather than risk foreclosure.
- Seek help from a credit counsellor or financial advisor for debt management strategies.
- Avoid quick fixes like payday loans or high-interest personal loans—they often worsen long-term financial health.
- Consider downsizing if other options fail. Selling before becoming delinquent allows more control over the process and outcome.
Long-Term Impacts on Canada’s Economy
The mortgage renewal crisis could have far-reaching effects:
- Lower household spending slows economic growth.
- Weaker real estate market performance, reducing government revenue from property taxes and transfer fees.
- Increased inequality, as younger or lower-income homeowners bear the brunt of rising costs.
This issue underscores the need for long-term housing affordability solutions and better financial literacy around borrowing and risk management.
Planning Ahead Is Key
The Canada mortgage renewal crisis isn’t just a short-term hiccup—it’s a systemic challenge affecting millions. Rising interest rates are transforming the homeownership landscape and reshaping household budgets nationwide.
Preparation is essential. Whether your mortgage renewal is months or years away, act now. Understanding your options, talking to professionals, and staying informed can protect your finances and keep your home secure in these turbulent times.









