Medical Debt Rebellion: States Defying Hospitals Over ‘Shadow Bills’ (Post-2024 Election Reforms)
Washington, D.C. – A new wave of healthcare reform is sweeping across the United States as multiple states launch a full-scale rebellion against the practice of issuing ‘shadow bills’—unregulated medical invoices sent to patients after insurance payments. The pushback, sparked by grassroots campaigns and accelerated by post-2024 election healthcare mandates, signals a potential seismic shift in the nation’s broken medical billing system.
What Are ‘Shadow Bills’?
‘Shadow bills’ refer to unofficial or unregulated medical invoices that hospitals send to patients, often after the insurance company has settled its portion. These bills—sometimes equal to or greater than the original cost—are neither standardized nor regulated by federal guidelines. Patients, thinking their expenses were covered, are shocked when they receive bills months later, demanding thousands more for “uncovered services” or “facility fees.”

In 2024 alone, over 18 million Americans received shadow bills totalling more than $16 billion, according to the National Healthcare Consumer Rights Coalition (NHCRC). With inflation, stagnant wages, and rising insurance deductibles, these unexpected charges have pushed many families further into medical debt or bankruptcy.
Post-Election Reforms: A Catalyst for Change
The 2024 U.S. presidential election placed healthcare affordability at the forefront of political discourse. Following the election, the newly elected administration introduced the Fair Medical Billing and Consumer Protection Act (FMBCPA) in early 2025, aiming to increase transparency and regulate medical billing practices across all states.
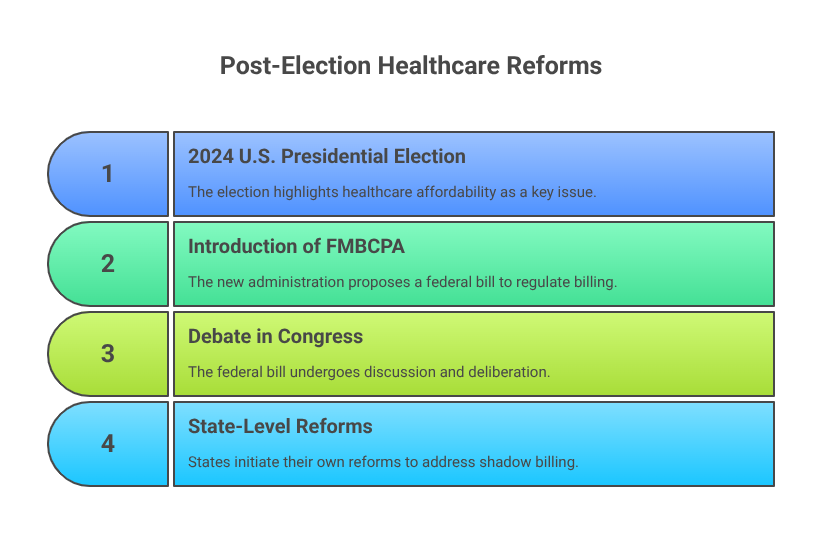
While the federal law is still being debated in Congress, many states are not waiting. Instead, they’re forging ahead with their own reforms—many directly targeting shadow billing.
California Leads the Charge
In March 2025, California became the first state to officially ban shadow billing under its Medical Debt Protection & Billing Transparency Act. The law mandates:
- Full disclosure of all charges before treatment (except in emergencies).
- A ban on sending separate facility fees unless pre-approved by insurance and signed off by the patient.
- Mandatory arbitration for disputed charges over $1,000.
California Attorney General Letitia Warren stated, “Hospitals cannot ambush patients with hidden charges months after care. We are putting an end to medical extortion disguised as billing.”
Since the bill’s passage, hospital lobbying groups like the California Healthcare Association (CHA) have filed lawsuits, arguing the law infringes on private contracts and threatens operational revenues. But public support remains high—with polls showing 78% of Californians backing the reform.
Other States Joining the Rebellion
Several other states have introduced or passed similar legislation in the past six months:
New York
New York’s “Clean Billing Act” goes into effect this August. It requires hospitals to provide a single, consolidated bill—including insurance and out-of-pocket expenses—with no secondary invoices allowed unless disclosed upfront.
Governor Laura Hernandez called the legislation “a direct response to systemic medical debt abuse.”
Colorado
In Colorado, the “Patient Billing Justice Act” was signed into law in April 2025. It allows patients to sue hospitals over shadow bills and provides funding for local legal aid groups to defend victims of medical overbilling.
Illinois, Oregon, and Massachusetts
All three states have either proposed bills or created commissions to investigate shadow billing practices and recommend regulatory frameworks by the end of 2025.
Hospitals Push Back
Hospital associations argue that shadow billing is a necessary mechanism to recover costs not covered by insurers—particularly as Medicare and Medicaid reimbursements lag behind actual service costs.
American Hospital Association (AHA) President Rick Maddox said in a statement, “These reforms, while well-intentioned, risk bankrupting community hospitals. The billing process is complex, and not all charges can be determined at the point of care.”
However, critics claim hospitals often use shadow bills as a revenue-maximizing strategy, exploiting the opaque healthcare pricing system and patients’ lack of bargaining power.
Patients Speak Out
The real cost of shadow bills is borne by patients like Kimberly West, a 36-year-old teacher from Phoenix, Arizona. After a routine gallbladder surgery in November 2024, she was billed $22,000 in unexpected facility fees months after her insurance had covered the procedure in full.
“I thought it was a scam,” West said. “But the hospital insisted it was legitimate. I’m still paying $400 a month just to keep them from sending debt collectors.”
Stories like Kimberly’s have become the rallying cry behind the #EndShadowBilling movement, which has gained momentum on social media and attracted support from consumer rights groups and legal advocates.
The Role of Technology in Reform
Some states are leveraging technology to combat shadow billing. Maryland and Washington State have introduced pilot programs requiring hospitals to integrate billing software with patient portals. This allows real-time tracking of charges and insurance adjustments—eliminating surprises down the line.
Tech companies are also entering the space. Startups like Bill Guard and Care Check offer AI-driven audits of hospital bills, helping patients flag duplicate charges, inflated fees, and unauthorized shadow billing.
Debt Forgiveness and Legal Relief
In tandem with reform legislation, several states are allocating emergency funds to forgive or pause medical debt incurred through shadow bills.
Illinois has partnered with non-profit organizations to buy and cancel over $350 million in medical debt, prioritizing low-income households.
Meanwhile, legal aid clinics across the country are seeing a surge in medical billing disputes. Some states are considering funding “medical debt ombudsman” offices to mediate between hospitals and consumers.
National Outlook: Will Congress Act?
While state-level action is gaining steam, a national solution remains elusive. The FMBCPA—originally backed by both parties—has become mired in partisan gridlock, with hospital lobbyists intensifying efforts to water down the legislation.
Still, the rebellion is having ripple effects. Senator Brian O’Malley (D-VT) recently introduced an amendment that would require hospitals to publish full price lists and insurance reimbursement rates online, further expanding transparency.
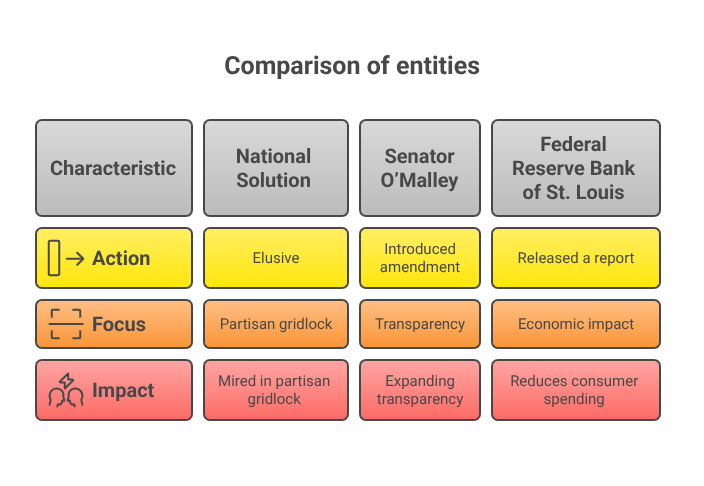
“There’s no such thing as a $75 Tylenol unless you live in a broken system,” O’Malley declared on the Senate floor. “Shadow bills are the symptom. Systemic greed is the disease.”
Economic Impact
Beyond individual hardship, the widespread use of shadow bills has macroeconomic consequences. The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis released a report this month stating that medical debt—much of it stemming from unregulated billing—reduces consumer spending by up to $22 billion annually.
The report also ties medical debt to decreased credit scores, housing instability, and increased bankruptcy filings.
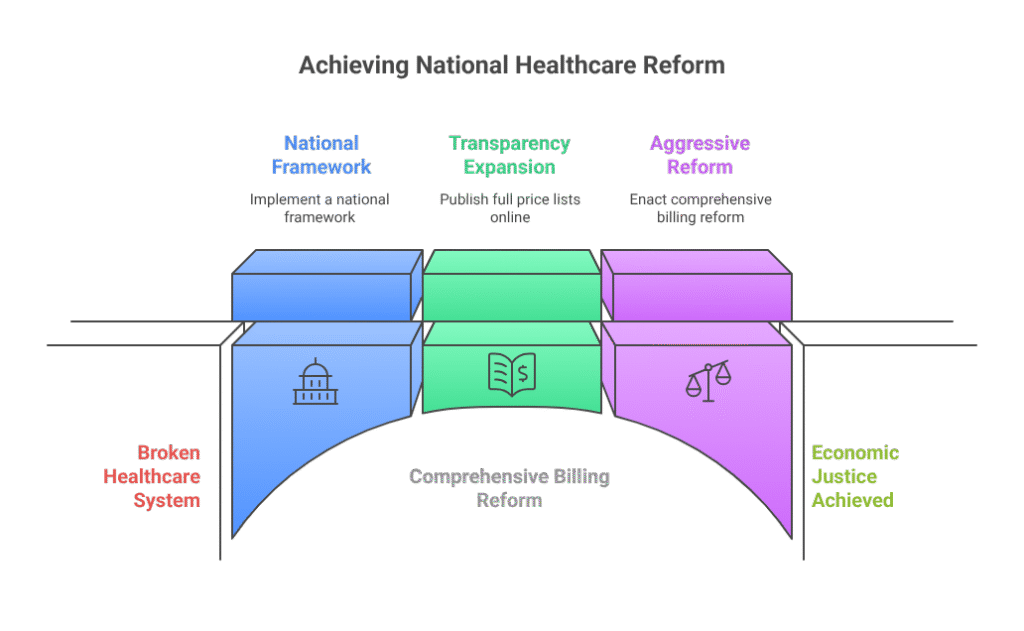
2025 and Beyond: A Healthcare Reckoning
As America continues to wrestle with the fallout from its fragmented healthcare system, the rebellion against shadow billing is becoming a defining moment in the fight for economic justice.
Advocates warn that without aggressive reform, the problem will persist. “You can’t fix a broken arm by covering it with a Band-Aid,” said Dr. Emily Carson, a policy expert at the Brookings Institution. “We need comprehensive billing reform and a national framework—not just state-by-state battles.”
Yet the states taking action are proving that change is possible—even in the face of powerful opposition. The medical debt rebellion is more than a legal fight; it’s a populist uprising demanding that American healthcare work for the people, not just for profit.